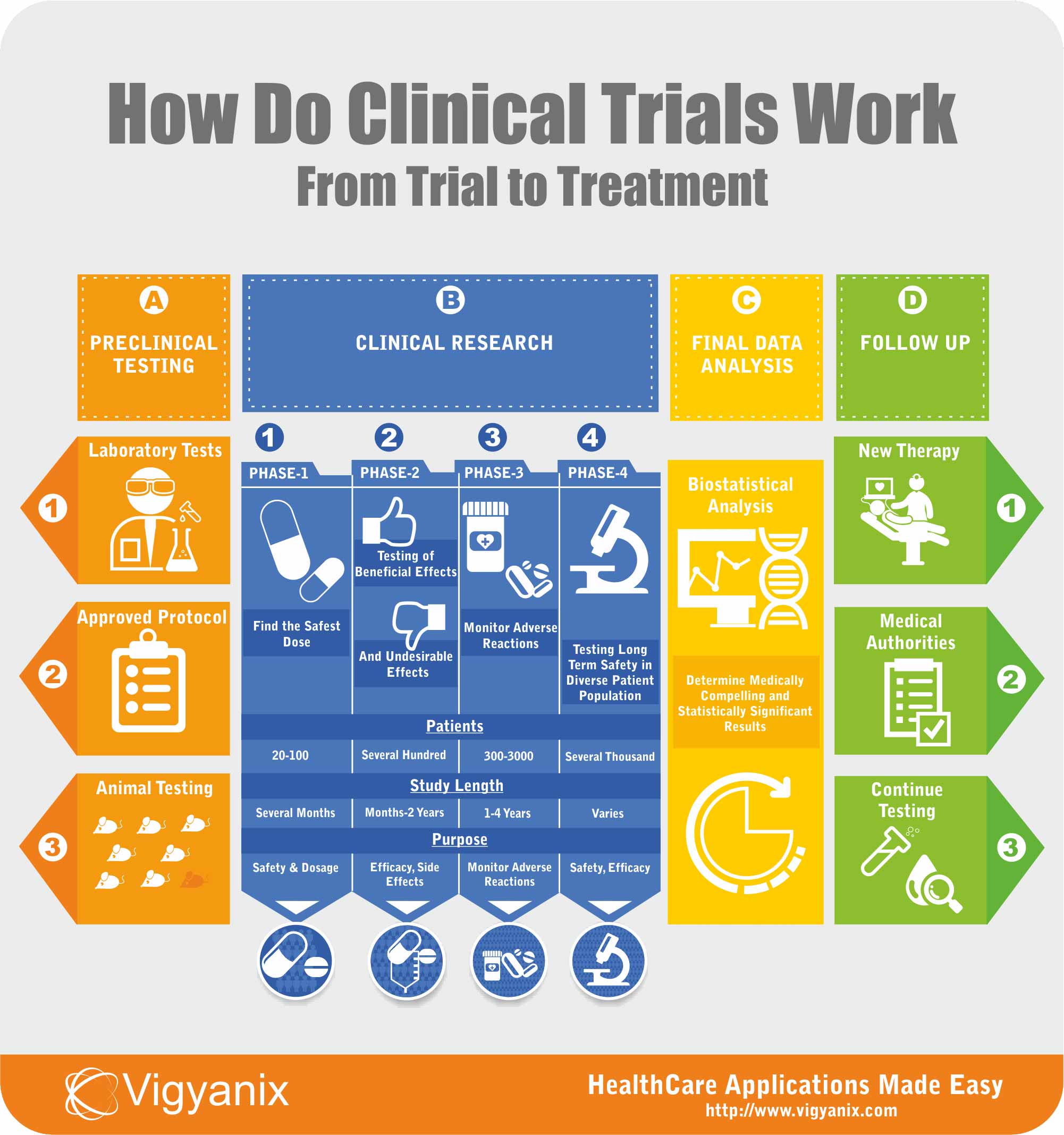
Clinical trials are conducted in order to gather more data regarding the safety and efficacy of a new drug or device development. There are several steps and stages of approval in the clinical trials process before a drug or device can be sold in the consumer market, if ever.
Drug and device testing begins with extensive laboratory research. If the initial laboratory research is successful, the data is then sent to FDA for approval to continue further testing on patients.
Once approved, human testing of experimental drugs and devices begins and is conducted in four phases. Each phase being a separate trial having a predefined objective.
Embed This Image On Your Site (copy code below):Clinical trials are conducted to get insight into what works and what doesn’t in medicine and health care. They are the best way to understand what works best in treating chronic diseases. Clinical trials are designed to answer two most important questions:
-
Does the new treatment work in humans? If it does, it’s important for physicians to find out how well it works. Is it better than treatment being used presently? If not, then is it reducing side effects? Clinical trials are intended to find diagnosis leading to improved treatment for chronic diseases.
-
Is the new treatment safe? Does the benefit of new treatment outweigh its possible risks. It’s well known that no treatment or procedure in common use is free of potential risks.
Answering all these questions requires several different trials, each having a different purpose and duration. Clinical trials are extensive research procedures – which involve years of experiments, thousands of patients – leading to better diagnosis and breakthrough in treatment of chronic diseases.